Acetylcholine iodide
CAS No. 2260-50-6
Acetylcholine iodide( Acetylcholine iodide, AI3-51677 )
Catalog No. M18267 CAS No. 2260-50-6
Acetylcholine iodide is a neurotransmitter found at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, parasympathetic effector junctions, a subset of sympathetic effector junctions, and at many sites in the central nervous system.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 52 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 84 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAcetylcholine iodide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAcetylcholine iodide is a neurotransmitter found at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, parasympathetic effector junctions, a subset of sympathetic effector junctions, and at many sites in the central nervous system.
-
DescriptionAcetylcholine iodide is an endogenous neurotransmitter at cholinergic synapses. Acetylcholine iodide amplifies the action potential of the sarcolemma thereby inducing muscle contractions.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAcetylcholine iodide, AI3-51677
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2260-50-6
-
Formula Weight273.11
-
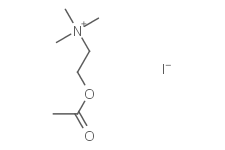
Molecular FormulaC7H16NO2·I
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : ≥ 100 mg/mL (366.15 mM))
-
SMILESCC(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C.[I-]
-
Chemical Name(2-Acetoxyethyl)trimethylammonium iodide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphen...
2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,6-methylenedioxybenzofuran (ABF).
-
CDDO-2P-Im
CDDO-2P-Im, an analog of CDDO-Imidazolide, has a chemopreventive effect. It can reduce the size and severity of the lung tumors in the mouse lung cancer model.
-
Dichotomitin
Dichotomitin is an isoflavonoid isolated from the rhizomes of?Belamcanda chinensis?(L.) DC.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


